|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Soil development depends on time. Under similar geo-ecologic conditions, soil type and soil characteristics vary according to the age of the soil and the corresponding parent material. Typical examples are soils on moraines, solifluction lobes, fluvial terraces, eolic deposits (sand, loess) or alluvial fans of different ages. |
1- Soil-moraine sequence |
| |
|
Paleosols were formed under different climatic conditions than today. Fossil soils are interbedded with sediments of different origin. The alteration of sedimentation and soil development indicates periods with varying paleoecologic conditions. |
2 - Paleosol-sediment sequence - Argentina (1.8MB) |
| Relictic soils were formed under different climatic conditions in the past, but are not or only slightly covered by younger sediments. Therefore, they are still influenced by modern weathering processes. Many surface soils in alpine regions are relictic soils.
|
3 - Paleosol-sediment sequence |
| |
|
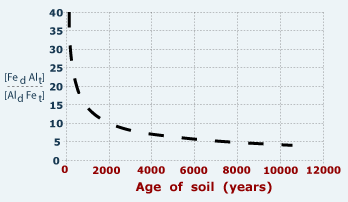
The weathering intensity of soils revealing information about past climate and soil age may be studied by applying various analytical methods, eg. texture analysis, measurement of Fe-, Al-oxides and hydroxides content (see fig. 4) and clay mineral analysis. |
4 - Fe-Al quotients in soils of different ages. to determine the age of soils, iron (Fe) and aluminum (AI) content in the soil has to bee measured. Using Fe-Al graph above, the age of soils can be determined. (material: moraines with granitic rocks (Alps), Egli et al. 2001) |
29 August 2011 |
||
| |
||
 Soils
develop slowly, especially in alpine regions. This makes them good indicators
of strongly reduced erosional processes for periods of hundreds or even
thousands of years, depending on the
Soils
develop slowly, especially in alpine regions. This makes them good indicators
of strongly reduced erosional processes for periods of hundreds or even
thousands of years, depending on the