|
|
|
|
|
|
|
At their upper limit (tree limit, tree line, forest limit, timberline, timberline ecotone) subalpine trees and forests exist under harsh conditions of life. Forests are characterized by a steady climate, by typical soil formation processes and by a forest flora adapted to these conditions.
|
|
For detailed information about these parameters see the links to other lessons. |
 1 1
 2 2
 3 3
 4 4 |
|
| 1 -Wind eroded Loiseleuria procumbens (wild azaleae spalier shrub)on a snow free mountain ridge in the subalpine belt (Schams valley, 2100m, Grisons, Switzerland). Photo: C. Burga (150K) |
| 2 - Avalanches, Klosters/Monbiel. Photo: H. Holzhauser (178K) |
| 3 - Debris flow cone on a forest free slope (coniferous forest of Pinus mugo s.l. / mountain pine on calcareous rocks, Swiss National Park). Photo: C. Burga (172K) |
| 4 - Subalpine Pinus contorta (lodgepole pine) forest ("toothpick forest") six years after the severe forest fire of 1988. Seedlings of rejuvenation grow between dead trees (Yellowstone N.P., Wyoming/USA). Photo: C Burga (172K) |
| |
|
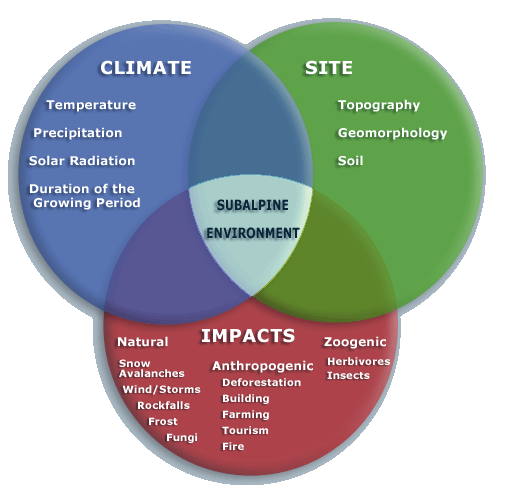
| Factors
influencing the Alpine environment |
|
| What strengths do the settlers (trees and stand of trees) show and what survival strategies are required ? Subalpine trees and forest plant communities
are very fragile biocoenosis; they use various survival strategies. Important
parameters are: |
|
|||
| Having identified the most important parameters limiting or inhibiting tree growth, the following section will focus on the habitus (facies) of the timberline ecotone. | |||
29 August 2011 |
||
| |
||