|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Alpine vegetation is the only terrestrial biogeographic unit with a global, but highly fragmented distribution. |
|
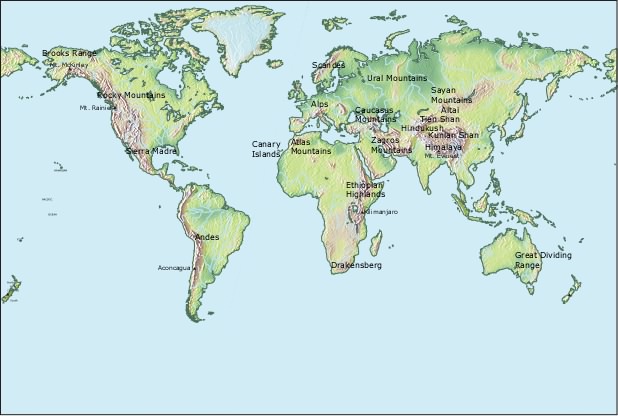
1 - Mountains and some high peaks |
|
Mountains vary widely in a origin, age, and developmental stage. This is why we can find smooth, rolling ranges that only reach low elevations but also rugged mountians with high peaks as well as symmetrical cones that result from volcanic activity. This varying geology and topography, together with the glaciation history, are important factors affecting the development of alpine ecosystems. Some mountains are hotspots of biodiversity. |
29 August 2011 |
||
| |
||