
On the map, several trends and answers to our research questions could be observed. In the following, we will focus on a limited amount of observations only. This section is divided into three different parts according to our three research questions:
For this part of the discussion, the focus is on the current situation which corresponds to data of 2020. The changes over time will be discussed in the next part. Regarding the literacy rate, we can see that it tends to be higher for males than for females. For men, only one country is ranked with a literacy rate below 40%, while for females it is 13 countries. This trend can also be seen when the difference of literacy rate between females and males is plotted (Fig. 1).
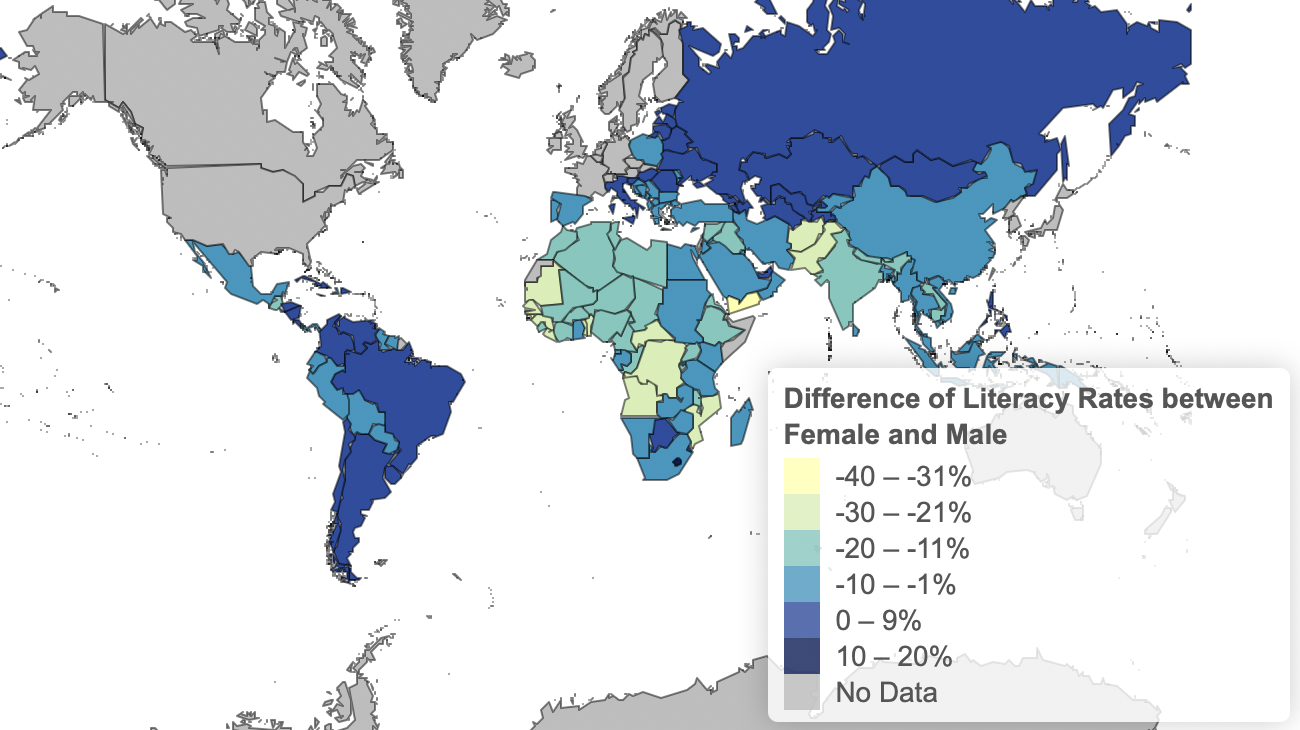
Fig. 1: Difference of Literacy Rate between Female and Male 2020
In most of the countries, males have a higher literacy rate than females, while only in a few countries it is the other way around. Examples are: Lesotho (17%), Jamaica (10%), and Uruguay (1%). There are also countries that have the same literacy rate for males and females (0%). Examples are: Russia, Brazil, and Italy.
For the labor force participation, we can see a similar trend. Overall, labour force participation for men is higher than for females. For males, the majority of countries have a participation rate higher than 50%. For females, this is not the case. Countries with a labour force participation below 50% are more widely distributed around the globe. Again, this trend can be observed by looking at the difference between both genders (Fig. 2).
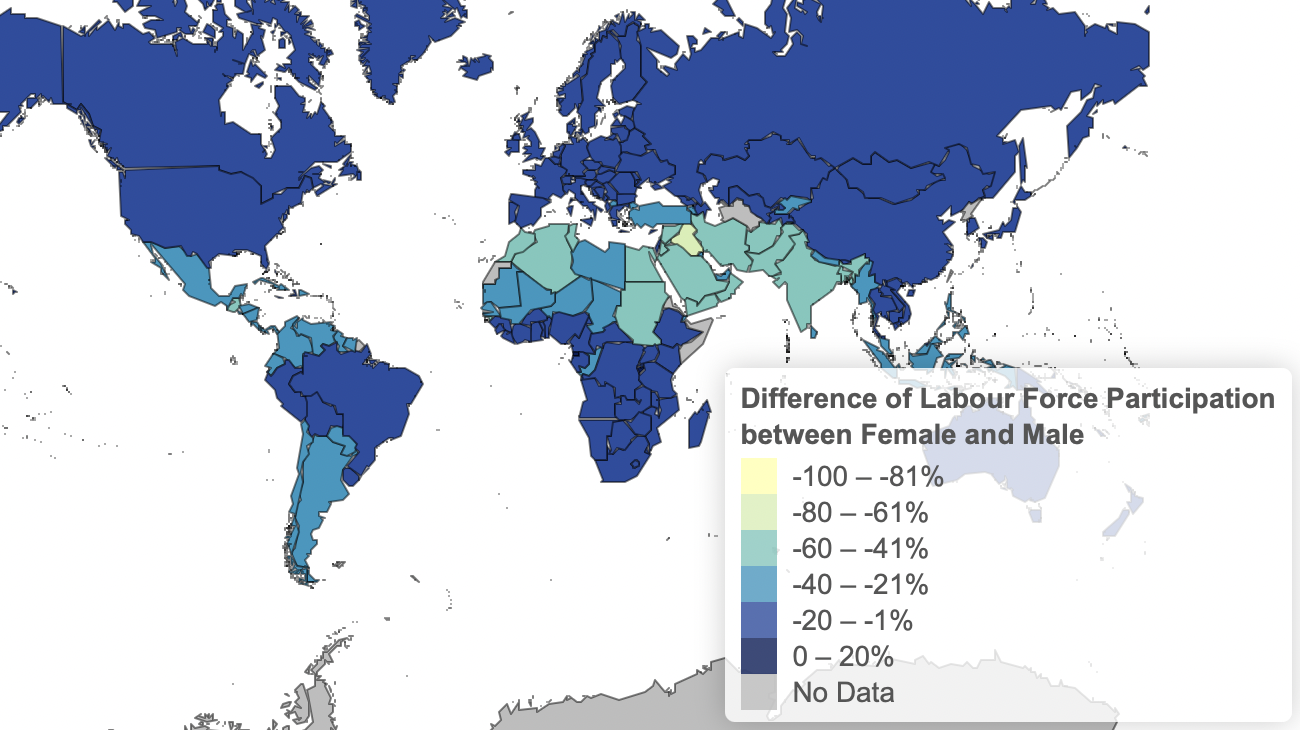
Fig. 2: Difference of Labour Force Participation between Female and Male 2020
The countries in the stretch between Morocco and India tend to have a greater difference regarding the labour force participation between the genders. The overall picture shows lower labour force participation for females than for males. Exceptions are Burundi (2%) and Equatorial Guinea (4%).
For a detailed analysis of the evolution over time, the slider in the visualization section can be used. This is especially useful if focusing on one specific country. Due to a lack of complete data, the temporal pattern is described for the change between 2000 and 2020 (Fig. 3 & 4).
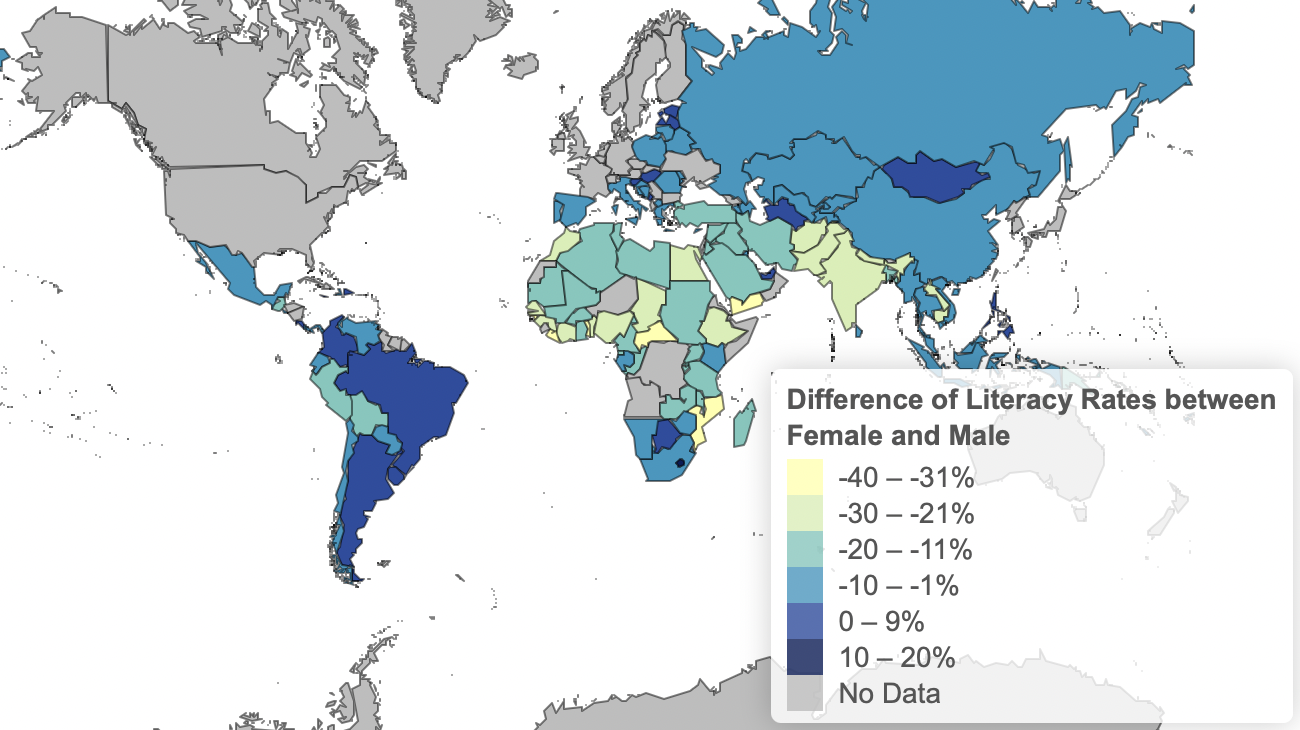
Fig. 3: Difference of Literacy Rates between Females and Males 2000

Fig. 4: Difference of Literacy Rates between Females and Males 2020
It can be observed that the difference of literacy rates between females and males has decreased. Many countries, such as Argentina, India, Mongolia, Morocco, Algeria have a smaller difference now than 20 years ago. This trend is also visible in the diagram where the worldwide literacy rate is plotted. There is a trend towards gender equality concerning literacy rates.
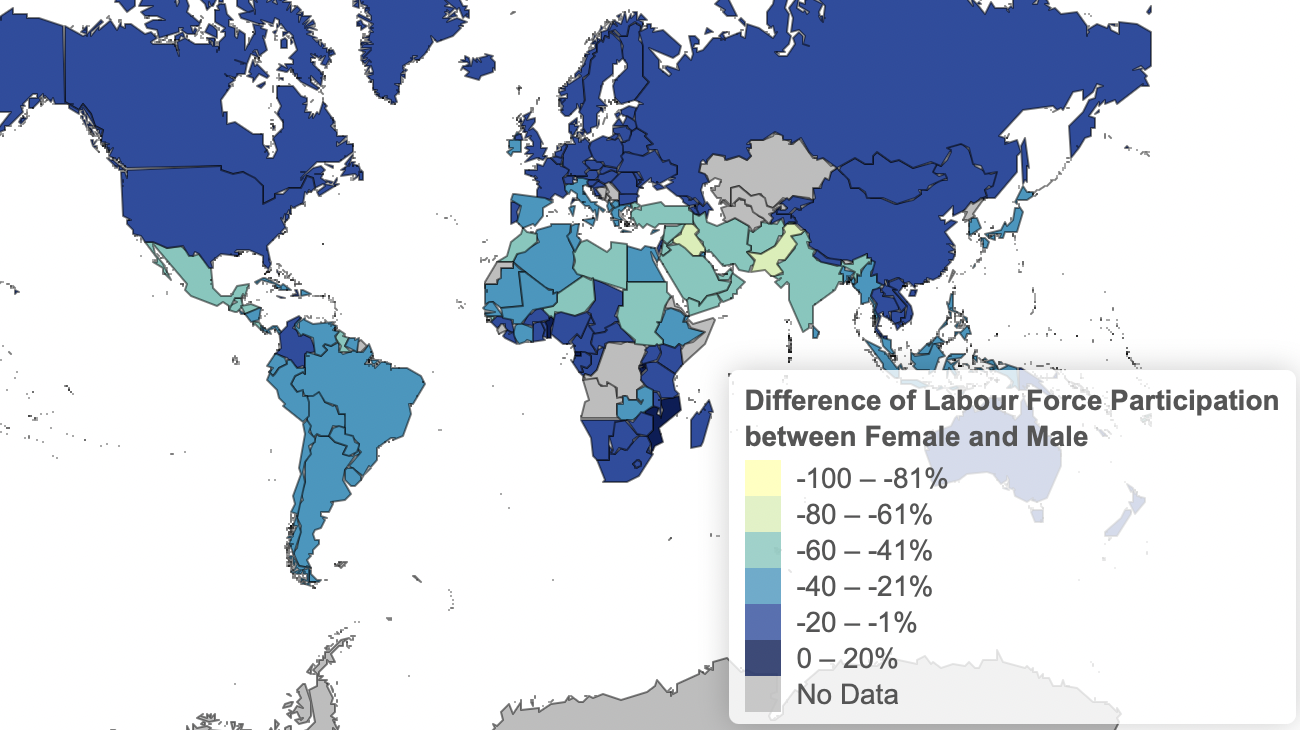
Fig. 5: Difference of Labour Participation between Females and Males 2000

Fig. 6: Difference of Labour Participation between Females and Males 2020
For the labour force participation (Fig. 5 & 6) the changes in the last 20 years were not striking. Worldwide the difference of labour force participation has not decreased, but in some countries, the situation has improved. Examples of countries in which the difference has decreased are: Mexico, Turkey, and Spain. For the labour force participation. A possible reason why the labour force participation rate did not improve as much as the literacy rate is that in many countries the labour force participation rate was already more balanced between the genders.
As already described, the countries in the stretch between Morocco and India have low gender equality, with respect to the two observed variables. Additionally, for literacy rate equatorial Africa is generally low.
The change in the past 20 years shows that there is improvement in achieving gender equality. Nevertheless, in many countries, especially the ones in the stretch between Morocco and India, much still needs to be done. But, we have to keep in mind that the great picture especially in labour force participation is not in favour of women, also in the global North, like for example Europe and North America. Another point worth to be mentioned is that gender equality entails way more than labour force participation and literacy rate. These two variables only show a small piece of the complex construct and dynamics of gender and gender equality.