|
||
 |
||
|
|
||
|
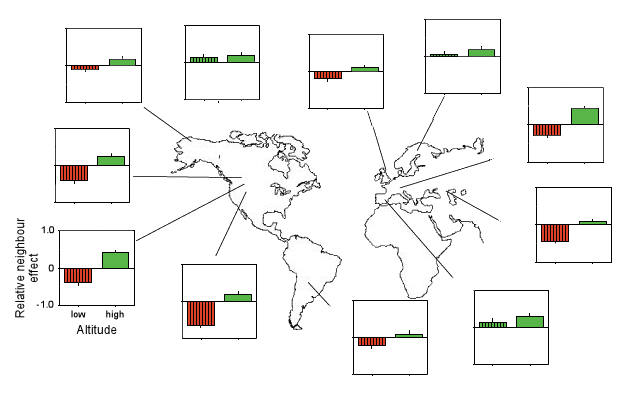
Relative neighbour effect (RNE) at eleven subalpine (hatched bars) and alpine (solid bars) sites, respectively
(after Callaway et al.,
2002)
|
||
|
Whereas the relative neighbour effect was negative at many of the subalpine sites, it was positive at all high altitude sites. Note that this is an overall effect, and that for particular species such as some cushion plants negative interactions may prevail. Interactions among plants were assessed by the removal of all
neighbouring species within 10 cm of a target individual, and comparison of the performance after two
growing seasons of target plants with neighbours removed to that of control plants around which
neighbours were left intact. |